Beginner's Guide to the Nutritarian Diet

One of the most powerful steps you can take to improve your health, boost energy levels, and prevent chronic diseases is to move to a plant-based, nutrient-dense Nutritarian diet. If you’ve read the New York Times bestseller, Eat to Live or Eat for Life, you know that the scientific evidence is clear: This eating style is a powerful way to lose weight, reverse chronic disease, live better, strengthen your immune defenses and slow the aging process.
Getting started is easy (and delicious!)
1. Read Eat for Life
If you haven't done so already, read my latest book Eat for Life. I will guide you through the science and show you the incredible power of nutritional excellence to prevent and reverse disease. The knowledge in this book will change your life forever and set you on the path to great health. On this website, you’ll find further tools, insight, and expertise to make the change easy and enjoyable. We’ve created products and strategies to help you, no matter what level of support you need. We’ll answer your questions, provide helpful advice, and empower you with proven strategies to embrace this healthy lifestyle.
On the website, you’ll find plenty of information, including our Success Stories and Health Concerns section which provides action plans and insights for a variety of health concerns. For a deeper dive, explore our membership options.
2. Keep learning and get support with membership
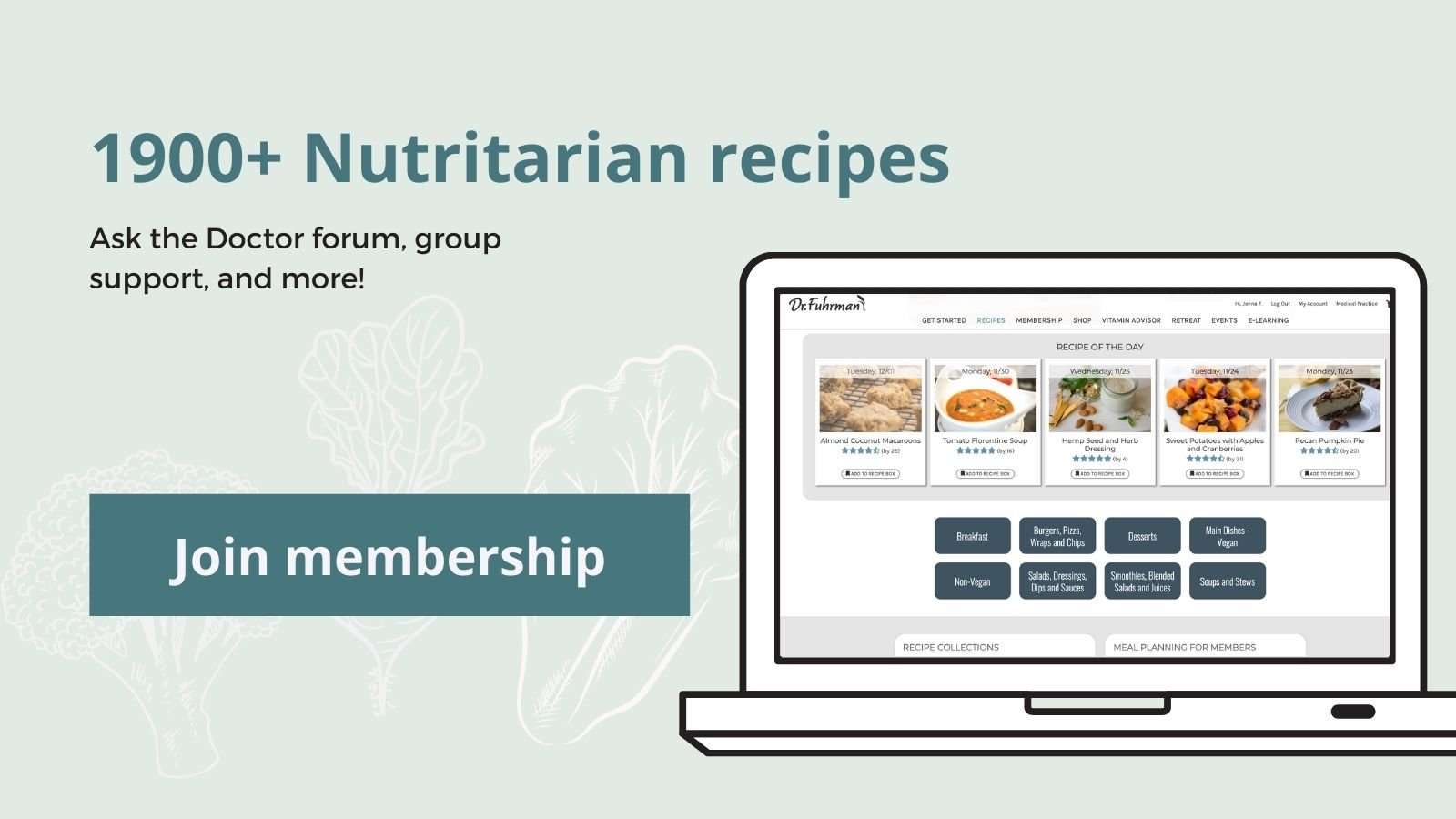
Membership to DrFuhrman.com will give you access to recipes, meal plans, grocery lists, group support, and education that will answer your questions and help you on your journey to superior health.
Let’s get down to the basics.
Can a plant-based diet, with no S.O.S. boost your health? YES!
There’s excellent scientific evidence that most chronic diseases can be reversed by a Nutritarian diet. Scientific research highlighted in Eat for Life, shows that a this nutrient-rich, plant-based diet can dramatically reduce the risk, and in many cases resolve type 2 diabetes, heart disease, autoimmune disease, certain types of cancer, and other major illnesses.
What is a Nutritarian diet?
This nutrient-rich, plant-based diet is based on the following principles:
- This eating style focuses on the nutrient-rich foods that unleash the body’s tremendous ability to heal, achieve optimal weight, and slow the aging process.
- Eat mostly plants means only eat animal products in small amounts, if any, such as meat, fish, dairy, and eggs
- Whole food describes natural foods that are not heavily processed. Basically, the majority of our diet is made up of fresh and clean produce rather than food that comes out of a package.
- No S.O.S. When we eat the whole nut over just the processed oil, we are eating the fiber and protective nutrients too!
Visit our recipe database to start eating like a nutritarian!

A Nutritarian diet meets your nutritional needs by focusing on natural, minimally processed plant foods and turning up the G-BOMBS! Nutritional research demonstrates these foods give us the greatest protection against cancer and other diseases.
What are G-BOMBS?
G-BOMBS is an acronym for Greens, Beans, Onions, Mushrooms, Berries and Seeds. These are the most health-promoting, anti-cancer superfoods on the planet. Make sure that you include some or all of them in your diet every day.

Greens: Greater consumption of these vegetables is linked to reduced risk of cancer and cardiovascular disease, and a longer life.
Beans: Beans and legumes are rich in fiber and resistant starch, which help keep blood glucose, blood pressure and LDL cholesterol down, and nourish the microbiome.
Onions: Onions and garlic are linked to a reduction in the risk of several cancers, and their distinctive sulfur-containing phytochemicals have a number of actions that benefit the cardiovascular system.
Mushrooms: Mushroom phytochemicals are unique in their promotion of immune system function with powerful anti-cancer benefits.
Berries: Berry phytochemicals have anti-cancer and blood pressure-lowering effects, and are linked to a reduced risk of heart attack.
Seeds: Eating raw seeds and nuts regularly is associated with longevity, reduced risk of cardiovascular disease, common cancers, and a healthy body weight.
You’ll love the benefits of a Nutritarian diet
3. Eat to Live with Dr. Fuhrman's famous Nutritarian recipes
The scientific evidence is clear. There are major benefits to moving to a Nutritarian diet.
- Optimal weight: People who eat a plant-based diet tend to be leaner than those who don’t, but a Nutritarian diet is undoubtedly the safest, healthiest and most effective way to do so. This diet makes it easy to lose weight and keep it off–without counting calories.
- Disease reversal and prevention: Whole-food, plant-based eating can prevent, halt, or even reverse chronic diseases, including heart disease, type 2 diabetes and autoimmune diseases.
- Immune Support: This eating style supplies the vital micronutrients and phytochemicals that help prevent inflammation and support normal immune function.
- Eco-friendly and sustainable: A plant-based diet places much less stress on the environment and can have a significant and positive impact on preventing climate change.
To compliment the Nutritarian diet, I have created a line of supplements to fill any nutritional gaps. It is imporant to supplement wisely. Your goal is to get adequate amounts of the nutritents not foundoptimally in a plant-based diet – such as vitamins B12 and D, plus the omega-3 fatty acids DHA/EPA – while avoiding potentially harmful ingredients, such as folic acid.
You’ll love the recipes!
Everyone puts their own twist on their favorite Nutritarian recipes, but here are some staples for your daily line up.
Dinner: Queso Dip with Carrots and Celery & Thai Curry






Looking for quick and easy recipes? Search our quick & easy tag in the recipe database.
4. Feel healthy, energetic and more vibrant as you lose excess weight
"I will guide you to superior health. Get started right now by signing up for my 5-Day Nutritarian Challenge! Enter your name and email below for daily tips and education."
At DrFuhrman.com we are wishing you the best of health!
References
- Zhang X, Shu XO, Xiang YB, et al. Cruciferous vegetable consumption is associated with a reduced risk of total and cardiovascular disease mortality.Am J Clin Nutr 2011, 94:240-246.
- Zurbau A, Au-Yeung F, Blanco Mejia S, et al. Relation of Different Fruit and Vegetable Sources With Incident Cardiovascular Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies.J Am Heart Assoc 2020, 9:e017728.
- Zhang Z, Bergan R, Shannon J, et al. The Role of Cruciferous Vegetables and Isothiocyanates for Lung Cancer Prevention: Current Status, Challenges, and Future Research Directions.Mol Nutr Food Res 2018, 62:e1700936.
- Hu J, Hu Y, Hu Y, Zheng S. Intake of cruciferous vegetables is associated with reduced risk of ovarian cancer: a meta-analysis.Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2015, 24:101-109.
- Wu QJ, Yang Y, Vogtmann E, et al. Cruciferous vegetables intake and the risk of colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis of observational studies.Ann Oncol 2013, 24:1079-1087.
- Wu QJ, Yang Y, Wang J, et al. Cruciferous vegetable consumption and gastric cancer risk: a meta-analysis of epidemiological studies.Cancer Sci 2013, 104:1067-1073.
- Liu X, Lv K. Cruciferous vegetables intake is inversely associated with risk of breast cancer: a meta-analysis.Breast 2013, 22:309-313.
- Jenkins DJ, Kendall CW, Augustin LS, et al. Effect of legumes as part of a low glycemic index diet on glycemic control and cardiovascular risk factors in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial.Arch Intern Med 2012, 172:1653-1660.
- Bazzano LA, Thompson AM, Tees MT, et al. Non-soy legume consumption lowers cholesterol levels: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Nutrition, metabolism, and cardiovascular diseases : NMCD 2011, 21:94-103.
- Streppel MT, Arends LR, van 't Veer P, et al. Dietary fiber and blood pressure: a meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials.Arch Intern Med 2005, 165:150-156.
- Sonnenburg JL, Backhed F. Diet-microbiota interactions as moderators of human metabolism.Nature 2016, 535:56-64.
- Kau AL, Ahern PP, Griffin NW, et al. Human nutrition, the gut microbiome and the immune system.Nature 2011, 474:327-336.
- O'Keefe SJ, Ou J, Aufreiter S, et al. Products of the colonic microbiota mediate the effects of diet on colon cancer risk.J Nutr 2009, 139:2044-2048.
- Sonnenburg ED, Sonnenburg JL. Starving our microbial self: the deleterious consequences of a diet deficient in microbiota-accessible carbohydrates.Cell Metab 2014, 20:779-786.
- Wan Q, Li N, Du L, et al. Allium vegetable consumption and health: An umbrella review of meta-analyses of multiple health outcomes.Food Sci Nutr 2019, 7:2451-2470.
- Galeone C, Pelucchi C, Levi F, et al. Onion and garlic use and human cancer.Am J Clin Nutr 2006, 84:1027-1032.
- Borchers AT, Krishnamurthy A, Keen CL, et al. The immunobiology of mushrooms.Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2008, 233:259-276.
- Akramiene D, Kondrotas A, Didziapetriene J, Kevelaitis E. Effects of beta-glucans on the immune system.Medicina (Kaunas) 2007, 43:597-606.
- Jeong SC, Koyyalamudi SR, Pang G. Dietary intake of Agaricus bisporus white button mushroom accelerates salivary immunoglobulin A secretion in healthy volunteers.Nutrition 2012, 28:527-531.
- Dai X, Stanilka JM, Rowe CA, et al. Consuming Lentinula edodes (Shiitake) Mushrooms Daily Improves Human Immunity: A Randomized Dietary Intervention in Healthy Young Adults.J Am Coll Nutr 2015, 34:478-487.
- Ba DM, Gao X, Al-Shaar L, et al. Prospective study of dietary mushroom intake and risk of mortality: results from continuous National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2003-2014 and a meta-analysis.Nutr J 2021, 20:80.
- Huang H, Chen G, Liao D, et al. Effects of Berries Consumption on Cardiovascular Risk Factors: A Meta-analysis with Trial Sequential Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Sci Rep 2016, 6:23625.
- Wang X, Ouyang YY, Liu J, Zhao G. Flavonoid intake and risk of CVD: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies.Br J Nutr 2014, 111:1-11.
- Kristo AS, Klimis-Zacas D, Sikalidis AK. Protective Role of Dietary Berries in Cancer.Antioxidants (Basel) 2016, 5.
- Grosso G, Yang J, Marventano S, et al. Nut consumption on all-cause, cardiovascular, and cancer mortality risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiologic studies.Am J Clin Nutr 2015, 101:783-793.
- Mayhew AJ, de Souza RJ, Meyre D, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of nut consumption and incident risk of CVD and all-cause mortality.Br J Nutr 2016, 115:212-225.
- Aune D, Keum N, Giovannucci E, et al. Nut consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease, total cancer, all-cause and cause-specific mortality: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies.BMC Med 2016, 14:207.
- Tindall AM, Petersen KS, Lamendella R, et al. Tree Nut Consumption and Adipose Tissue Mass: Mechanisms of Action.Curr Dev Nutr 2018, 2:nzy069.
- Le LT, Sabate J. Beyond meatless, the health effects of vegan diets: findings from the Adventist cohorts.Nutrients 2014, 6:2131-2147.
- Tonstad S, Butler T, Yan R, Fraser GE. Type of vegetarian diet, body weight, and prevalence of type 2 diabetes.Diabetes Care 2009, 32:791-796.
- Alwarith J, Kahleova H, Rembert E, et al. Nutrition Interventions in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Potential Use of Plant-Based Diets. A Review.Front Nutr 2019, 6:141.
- Escalante-Araiza F, Rivera-Monroy G, Loza-Lopez CE, Gutierrez-Salmean G. The effect of plant-based diets on meta-inflammation and associated cardiometabolic disorders: a review.Nutr Rev 2022.
- Kim H, Caulfield LE, Garcia-Larsen V, et al. Plant-Based Diets Are Associated With a Lower Risk of Incident Cardiovascular Disease, Cardiovascular Disease Mortality, and All-Cause Mortality in a General Population of Middle-Aged Adults.J Am Heart Assoc 2019, 8:e012865.
- Knippenberg A, Robinson GA, Wincup C, et al. Plant-based dietary changes may improve symptoms in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.Lupus 2022, 31:65-76.
- Loeb S, Fu BC, Bauer SR, et al. Association of Plant-Based Diet Index with Prostate Cancer Risk.Am J Clin Nutr 2021.
- Patel H, Chandra S, Alexander S, et al. Plant-Based Nutrition: An Essential Component of Cardiovascular Disease Prevention and Management.Curr Cardiol Rep 2017, 19:104.
- Romanos-Nanclares A, Willett WC, Rosner BA, et al. Healthful and Unhealthful Plant-Based Diets and Risk of Breast Cancer in U.S. Women: Results from the Nurses' Health Studies.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2021, 30:1921-1931.
- Satija A, Bhupathiraju SN, Rimm EB, et al. Plant-Based Dietary Patterns and Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes in US Men and Women: Results from Three Prospective Cohort Studies.PLoS Med 2016, 13:e1002039.
- Satija A, Bhupathiraju SN, Spiegelman D, et al. Healthful and Unhealthful Plant-Based Diets and the Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in U.S. Adults.J Am Coll Cardiol 2017, 70:411-422.
- Dinu M, Abbate R, Gensini GF, et al. Vegetarian, vegan diets and multiple health outcomes: A systematic review with meta-analysis of observational studies.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2017, 57:3640-3649.
- Yokoyama Y, Barnard ND, Levin SM, Watanabe M. Vegetarian diets and glycemic control in diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cardiovasc Diagn Ther 2014, 4:373-382.
- Fuhrman J, Singer M. Improved Cardiovascular Parameter With a Nutrient-Dense, Plant-Rich Diet-Style: A Patient Survey With Illustrative Cases.Am J Lifestyle Med 2017, 11:264-273.
- Dunaief DM, Fuhrman J, Dunaief JL, Ying G. Glycemic and cardiovascular parameters improved in type 2 diabetes with the high nutrient density (HND) diet.OJPM 2012, 2.
- Fuhrman J, Sarter B, Calabro DJ. Brief case reports of medically supervised, water-only fasting associated with remission of autoimmune disease.Altern Ther Health Med 2002, 8:112, 110-111.
- Linus Pauling Institute Micronutrient Information Center. Immunity in Depth [https://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/health-disease/immunity]
- Yahfoufi N, Alsadi N, Jambi M, Matar C. The Immunomodulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Role of Polyphenols.Nutrients 2018, 10.
- Hooper LV. You AhR what you eat: linking diet and immunity.Cell 2011, 147:489-491.
- Lau BH, Yamasaki T, Gridley DS. Garlic compounds modulate macrophage and T-lymphocyte functions.Molecular Biotherapy 1991, 3:103-107.
- Hassan ZM, Yaraee R, Zare N, et al. Immunomodulatory affect of R10 fraction of garlic extract on natural killer activity.Int Immunopharmacol 2003, 3:1483-1489.
- Choy KW, Murugan D, Leong XF, et al. Flavonoids as Natural Anti-Inflammatory Agents Targeting Nuclear Factor-Kappa B (NFkappaB) Signaling in Cardiovascular Diseases: A Mini Review.Front Pharmacol 2019, 10:1295.
- Oregon State University. Linus Pauling Institute: Micronutrient Information Center. Flavonoids. [https://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/dietary-factors/phytochemicals/flavonoids]
- Hosseinzade A, Sadeghi O, Naghdipour Biregani A, et al. Immunomodulatory Effects of Flavonoids: Possible Induction of T CD4+ Regulatory Cells Through Suppression of mTOR Pathway Signaling Activity.Front Immunol 2019, 10:51.
- Patel S, Vajdy M. Induction of cellular and molecular immunomodulatory pathways by vitamin A and flavonoids.Expert Opin Biol Ther 2015, 15:1411-1428.
- Askarpour M, Karimi M, Hadi A, et al. Effect of flaxseed supplementation on markers of inflammation and endothelial function: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Cytokine 2020, 126:154922.
- Milani A, Basirnejad M, Shahbazi S, Bolhassani A. Carotenoids: biochemistry, pharmacology and treatment.Br J Pharmacol 2017, 174:1290-1324.
- Katz DL. Plant-Based Diets for Reversing Disease and Saving the Planet: Past, Present, and Future.Adv Nutr 2019, 10:S304-S307.
- Willett W, Rockstrom J, Loken B, et al. Food in the Anthropocene: the EAT-Lancet Commission on healthy diets from sustainable food systems.Lancet 2019, 393:447-492.

Joel Fuhrman, M.D. is a board-certified family physician, seven-time New York Times bestselling author and internationally recognized expert on nutrition and natural healing, who specializes in preventing and reversing disease through nutritional methods. Dr. Fuhrman coined the term “Nutritarian” to describe his longevity-promoting, nutrient dense, plant-rich eating style.
For over 30 years, Dr. Fuhrman has shown that it is possible to achieve sustainable weight loss and reverse heart disease, diabetes and many other illnesses using smart nutrition. In his medical practice, and through his books and PBS television specials, he continues to bring this life-saving message to hundreds of thousands of people around the world.












